Posted on Tuesday, November 11, 2025
Every roll forming machine relies on a precisely designed electrical control and wiring system. This system ensures that motors, sensors, drives, and hydraulic units operate in perfect synchronization to deliver accuracy, efficiency, and safety.
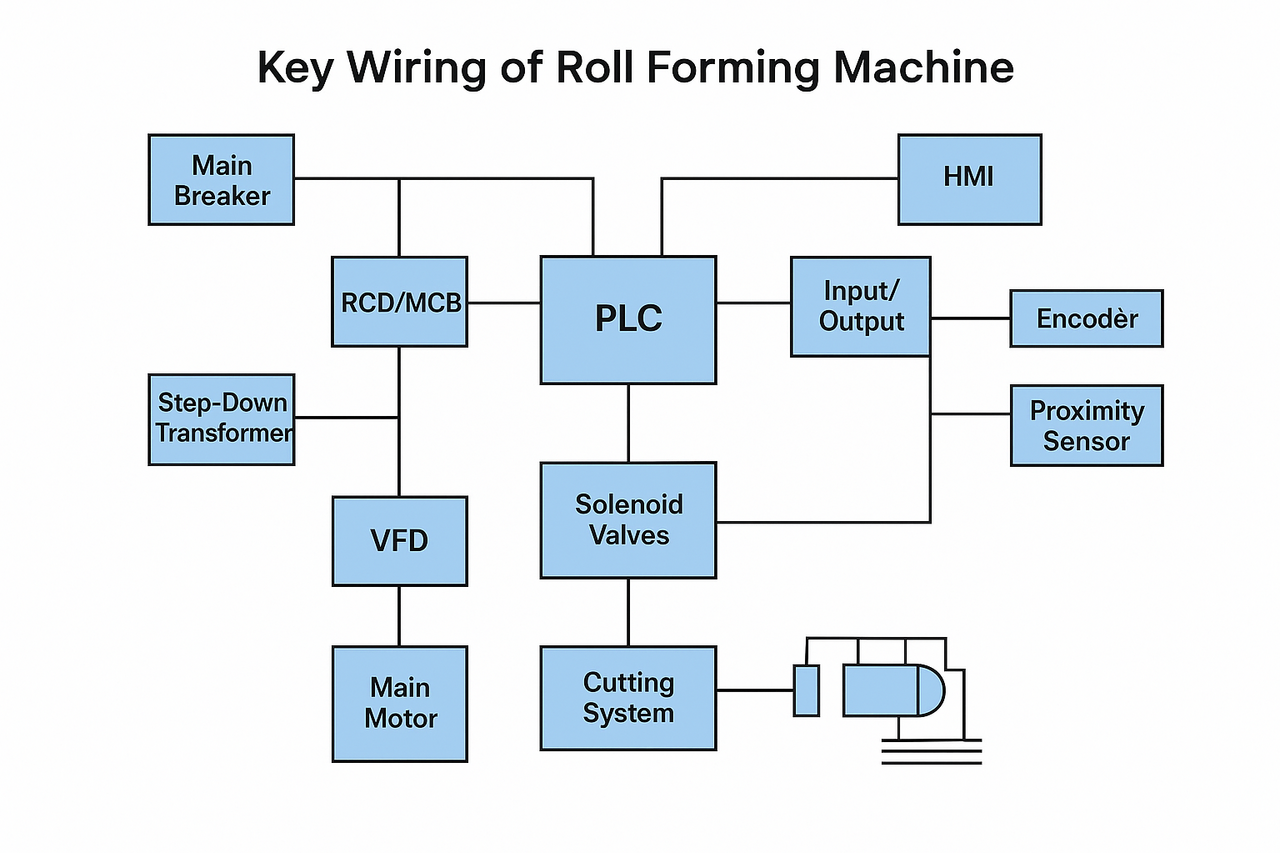
In this guide, we’ll break down the key wiring layout, main control panel components, and how everything connects — from the main power isolator to the PLC and sensors on the production line.
The main power circuit distributes electrical energy from the facility’s supply to all critical parts of the roll forming line.
Key Components:
Main Isolator / Circuit Breaker: The main disconnect switch for the entire machine.
RCD / MCB / MCCB: Protects against overload and short-circuits.
Step-Down Transformer: Converts 380–415V 3-phase AC to 24V DC control voltage.
Power Busbars & Distribution Blocks: Supply power evenly to all drives and control units.
Grounding Busbar: Ensures operator and system safety.
Voltage Standards:
Industrial machines typically run at 380–415V AC, 3-phase.
Control circuits operate at 24V DC.
At the heart of every modern roll forming line is a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller).
It governs all sequences — from coil feeding to cutting.
Main Components:
PLC CPU & I/O Cards: Handle all machine logic and feedback.
Input Modules: Receive signals from sensors and switches.
Output Modules: Activate relays, drives, and solenoid valves.
HMI (Human Machine Interface): Touchscreen for operation and status monitoring.
Power Supply Unit (24V DC): Feeds PLC, relays, and sensors.
Common Connections:
Digital Inputs: Start, Stop, Emergency Stop.
Digital Outputs: Motor relays, hydraulic valves.
Analog Signals: Length sensors, pressure, or speed reference.
Communication Lines: Ethernet or RS485 between PLC, HMI, and drives.
The motor wiring system powers all movement in the roll forming machine — forming, feeding, cutting, and stacking.
Key Elements:
Main Drive Motor: Turns the forming rollers.
VFD (Variable Frequency Drive): Controls motor speed and direction.
Servo Drives: Manage flying shear or punching units with precision.
Hydraulic Pump Motor: Powers cutting or notching systems.
Control Flow Example:
PLC → Output Signal → Contactor → VFD → Main Motor
Each drive receives feedback from the encoder to synchronize cutting and feeding operations.
Sensors are the “eyes” of the roll forming line, constantly feeding live data to the PLC.
Typical Devices:
Proximity Sensors: Detect sheet position or metal presence.
Photoelectric Sensors: Identify sheet ends or feeding gaps.
Limit Switches: Define travel limits for mechanical parts.
Encoder: Measures line speed and sheet length.
Pressure & Temperature Sensors: Monitor hydraulic systems.
Standard Sensor Wiring:
3-Wire Sensors: Brown (+24V), Blue (0V), Black (Signal).
Encoders: 5–6 wires (A, B, Z, +24V, GND).
Hydraulic and pneumatic controls manage forming dies, cutters, and punches.
Components:
Solenoid Valves (24V DC): Operate cylinders for cutting/punching.
Pressure Switches: Send status feedback to PLC.
Hydraulic Pump Starter: Controls pump motor through contactor and relay.
Typical Control Path:
PLC Output → Relay → Solenoid Valve → Cylinder Activation
Safety circuits protect both operator and equipment.
Common Safety Devices:
Emergency Stop Buttons: Wired in series, normally closed.
Safety Relays: Monitor E-stop and interlock integrity.
Door Interlock Switches: Disable operation if the panel door is open.
Overheat Sensors: Protect motors and drives from high temperatures.
Alarm Indicators: Buzzer and signal lights for warnings.
Logic:
When an emergency stop is pressed → PLC output disables → main contactor drops → power to all drives is cut.
Many roll forming lines now include remote monitoring and diagnostics systems for real-time support.
Typical Communication Setup:
PLC ↔ HMI: Ethernet or RS232.
PLC ↔ VFD / Servo Drive: Modbus RS485 or CANopen.
Remote Access Module: Ewon, PLCRemote.net, or similar device.
Ethernet Switch: Connects PLC, HMI, and external access modules.
This allows Machine Matcher engineers to provide remote troubleshooting and PLC code updates globally.
| Section | Main Components |
|---|---|
| Power Input | Main isolator, MCCB, RCD/MCB, surge protectors |
| Control Power | Transformer, 24V DC power supply |
| Drives | VFDs, servo drives, overload relays |
| PLC Section | PLC CPU, I/O modules, expansion cards |
| Safety Section | Safety relay, E-stop loop, interlocks |
| Hydraulic Control | Pump contactor, solenoid relays |
| I/O Field Wiring | Terminal blocks, labeling strips |
| Networking | Ethernet switch, remote access device |
| Cooling | Fans, filters, panel heater (if needed) |
A properly designed panel separates:
Power section (left)
Control & PLC section (center)
Communication and safety section (right)
This ensures reduced electromagnetic interference and simplified maintenance.
Cable ducts, wire numbering, and grounding improve safety and compliance.
| Circuit Type | Wire Size (mm²) | Voltage | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Power | 6–25 mm² | 380–415V | Motor and supply |
| Control Circuit | 0.75–1.5 mm² | 24V DC | PLC and sensors |
| Signal / Encoder | 0.5–0.75 mm² | 24V DC | Shielded cable |
| Communication | CAT6 / RS485 | Low Voltage | Shielded twisted pair |
[Main Breaker] → [RCD/MCB] → [VFD] → [Main Motor]
↘ [PLC + 24V PSU] → [Inputs/Outputs]
↘ [Encoder] → [PLC Input Module]
↘ [Solenoid Valves] → [Cutting System]
UPS Backup Unit: Prevents control loss during power flickers.
Data Logger or SCADA Gateway: Records production data.
Power Analyzer: Monitors energy efficiency.
Remote Camera Monitoring: Enables live view of machine status.
AI Diagnostics via Machine Matcher: For predictive maintenance and PLC fault analysis.
Inspect cable connections monthly for loosened terminals.
Clean filters and fans to prevent overheating.
Check drive parameters after software updates.
Test E-stop and safety loops weekly.
Document wiring changes in the schematic diagram.
The electrical system of a roll forming machine is the backbone of precision, reliability, and safety.
From main power distribution to PLC automation, every wire and connection plays a critical role in ensuring the line runs smoothly.
A properly designed and maintained panel reduces downtime, simplifies troubleshooting, and extends machine lifespan.
Machine Matcher supplies fully wired, PLC-ready roll forming machines — designed, tested, and supported globally.
We also provide remote technical support, PLC diagnostics, and full wiring schematics for every machine we deliver.


Used Purlin Roll Forming Machines for Sale Worldwide
Posted on Sunday, January 25, 2026
Pre-Owned Roll Forming Machines for Purlin & Structural Steel Profiles

Used Roof Panel Roll Forming Machines for Sale Worldwide
Posted on Sunday, January 25, 2026
Pre-Owned Roll Forming Machines for Roofing Panel Production

Used Roll Forming Machines for Sale Worldwide
Posted on Tuesday, January 20, 2026
Pre-Owned Roll Forming Machines with Inspection, Verification & Global Support

Steel Coil Supply for Roll Forming Machines Worldwide
Posted on Tuesday, January 20, 2026
Reliable Steel Coil Supply for Roll Forming, Fabrication & Manufacturing Applications
Copyright 2026 © Machine Matcher.