Posted on Friday, May 23, 2025
1. Introduction to Metal Flashing
Metal flashing is a thin layer of impervious material installed to prevent the passage of water into a structure from an angle or joint. Whether used on roofs, walls, windows, or doors, flashing plays a vital role in moisture control, preventing leaks that can lead to structural damage and mold. Historically developed from lead and copper, today’s flashing solutions span multiple metals and are key to long-term building integrity.
Flashing is essential in both residential and commercial buildings, forming a critical barrier in the building envelope. It ensures rainwater is directed away from seams, corners, and edges where water intrusion is most likely.
2. Materials Used in Metal Flashing
Galvanized Steel: One of the most widely used materials, galvanized steel is coated with a layer of zinc to prevent corrosion. It is cost-effective and suitable for most climates but may eventually corrode in coastal or highly acidic environments.
Aluminum: Lightweight and naturally rust-resistant, aluminum is ideal for coastal regions. It is easily formed and cut but can be prone to galvanic corrosion when in contact with other metals.
Copper: Known for its durability and aesthetic appeal, copper flashing develops a patina over time that adds to its weather resistance. It is often used in high-end residential or historical restoration projects.
Stainless Steel: This material offers exceptional resistance to corrosion and strength. It's commonly used in harsh climates or where chemical exposure is a concern.
Zinc: With a natural self-healing patina, zinc is both long-lasting and environmentally friendly. It is more expensive but preferred in modern and sustainable architecture.
Lead-Coated Copper: This hybrid material combines the flexibility of lead and the strength of copper, offering excellent weather protection and ease of installation.
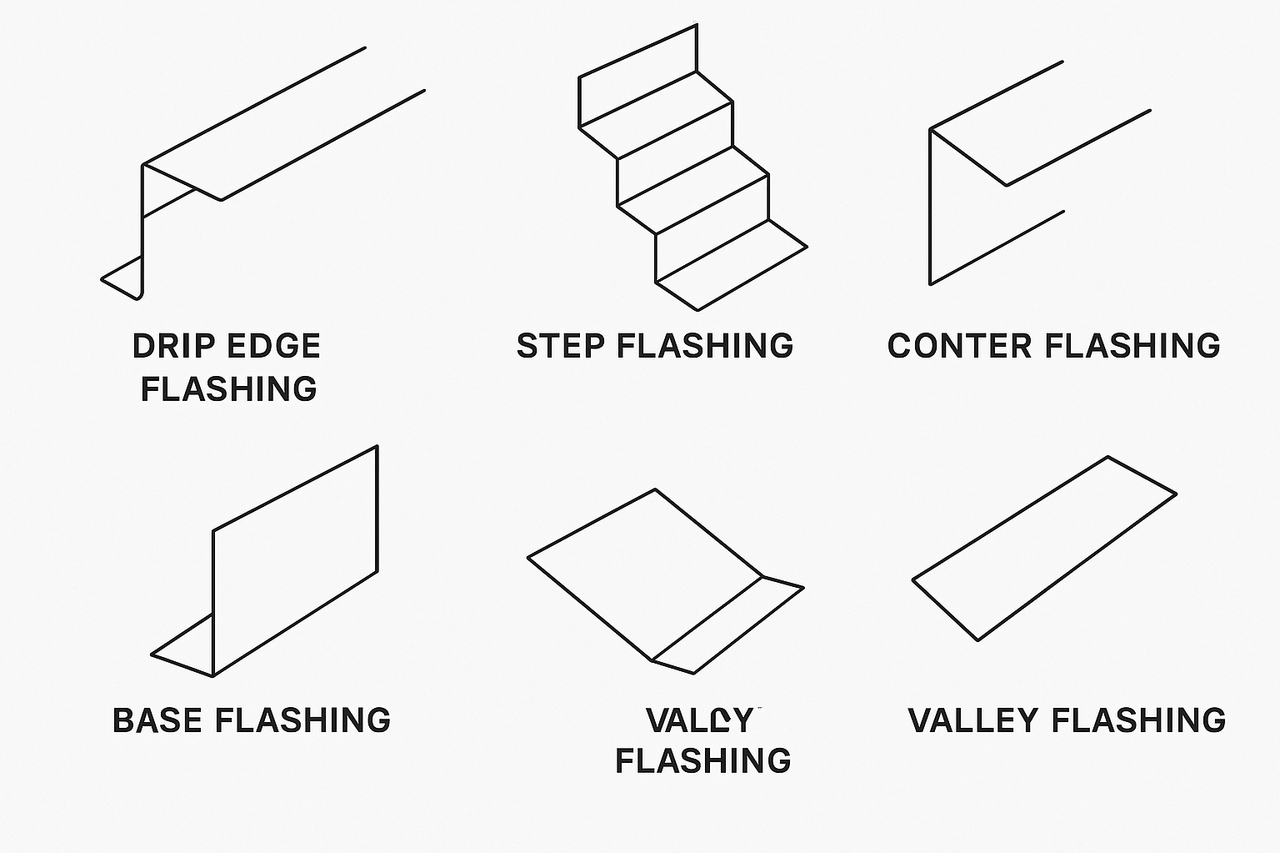
3. Metal Flashing Profile Types
There are many types of metal flashing profiles, each designed for specific architectural functions:
4. Standard Sizes and Custom Dimensions
Metal flashing comes in a range of standard and custom sizes:
Custom dimensions can be fabricated based on project specifications, ensuring a precise fit and optimal performance. Some regions have specific size standards based on local building codes and material availability.
5. Common Applications of Metal Flashing
Metal flashing is used in a variety of architectural and industrial applications:
6. Industries That Use Metal Flashing
7. Advantages of Metal Flashing
8. Installation Tips and Best Practices
9. Challenges and Mistakes to Avoid
10. Maintenance and Inspection
11. Environmental and Green Building Aspects
12. Top Manufacturers in the USA
13. Top 20 Global Metal Flashing Manufacturers
14. Conclusion
Metal flashing is one of the most critical elements in protecting a building envelope from the elements. Choosing the right material and profile, ensuring proper installation, and working with reputable manufacturers can greatly extend the life of any structure. Whether you're an architect, contractor, or building owner, understanding metal flashing fundamentals is a long-term investment in your project’s success.
15. FAQs
Q: What gauge is best for roof flashing? A: 26 to 22 gauge for steel is common; aluminum is often .019" to .032".
Q: Can aluminum flashing be used with steel roofing? A: It's not recommended due to galvanic corrosion risks unless properly isolated.
Q: How long does metal flashing last? A: With proper installation, 30+ years for galvanized, 50+ for copper or stainless steel.
Q: Does metal flashing need to be painted? A: Some materials benefit from painting; others like copper and stainless do not.
Q: What is the cost difference between copper and aluminum flashing? A: Copper can be 5-10x more expensive, but also offers superior longevity and appearance.

Used Purlin Roll Forming Machines for Sale Worldwide
Posted on Sunday, January 25, 2026
Pre-Owned Roll Forming Machines for Purlin & Structural Steel Profiles

Used Roof Panel Roll Forming Machines for Sale Worldwide
Posted on Sunday, January 25, 2026
Pre-Owned Roll Forming Machines for Roofing Panel Production

Used Roll Forming Machines for Sale Worldwide
Posted on Tuesday, January 20, 2026
Pre-Owned Roll Forming Machines with Inspection, Verification & Global Support

Steel Coil Supply for Roll Forming Machines Worldwide
Posted on Tuesday, January 20, 2026
Reliable Steel Coil Supply for Roll Forming, Fabrication & Manufacturing Applications
Copyright 2026 © Machine Matcher.